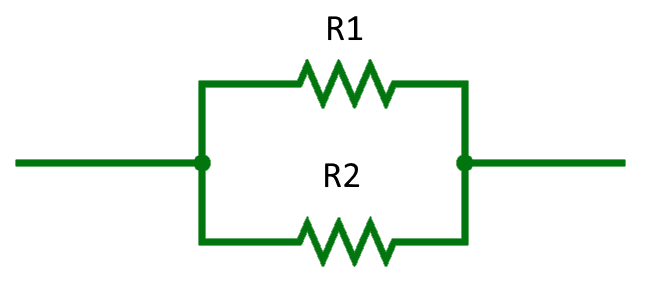
Range of Power for Parallel Resistors
When replacing a single resistor with an equivalent pair of resistors in parallel, the total resistance of the combination will be the same as the original resistor.However, power handling capability of the new parallel combination can differ from that of the original resistor. Consider this:
Total Resistance Calculation: For two resistors, \( R_1 \) and \( R_2 \), in parallel, the equivalent resistance \( R_{eq} \) is given by:
Power Distribution: The power dissipated in a resistor is given by \( P = \frac{V^2}{R} \), where \( V \) is the voltage across the resistor. For the parallel combination, each resistor has same voltage across them.
Power Sharing: If \( P_1 \) and \( P_2 \) are the powers dissipated by resistors \( R_1 \) and \( R_2 \) respectively, then:
The total power dissipated by the parallel combination \( P_{total} \) is:
Power Rating of Individual Resistors: The power rating of the new resistors in parallel must be selected such that neither of them exceeds its maximum rated power. Let's suppose that the original resistor had a power rating \( P_{original} \).
Minimum Power Rating: The minimum power rating of each resistor in the parallel combination must be sufficient to handle its share of the total power. For equal resistors (\( R_1 = R_2 \)):
Therefore, each resistor must have a power rating of at least \( \frac{P_{original}}{2} \).
General Case: For resistors of different values, the power rating of each resistor has to be determined considering the ratio of their resistances. For resistors \( R_1 \) and \( R_2 \):
Example: 150 Ω and 180 Ω Resistors in Parallel
Let's analyze an example where a 150 Ω resistor is in parallel with another of 180 Ω. We will calculate the equivalent resistance and the power ratings for each resistor.
Total Resistance Calculation: For two resistors, \( R_1 = 150 \, \Omega \) and \( R_2 = 180 \, \Omega \), in parallel, the equivalent resistance \( R_{eq} \) is given by:
Power Distribution: If the total power applied is \( P_{total} \), the power dissipated in each resistor can be found using:
Example Calculation: Consiter that the total power \( P_{total} \) is 10 W.
Power Rating of Individual Resistors: Each resistor must have a power rating that can handle at least its share of the total power. In this example: